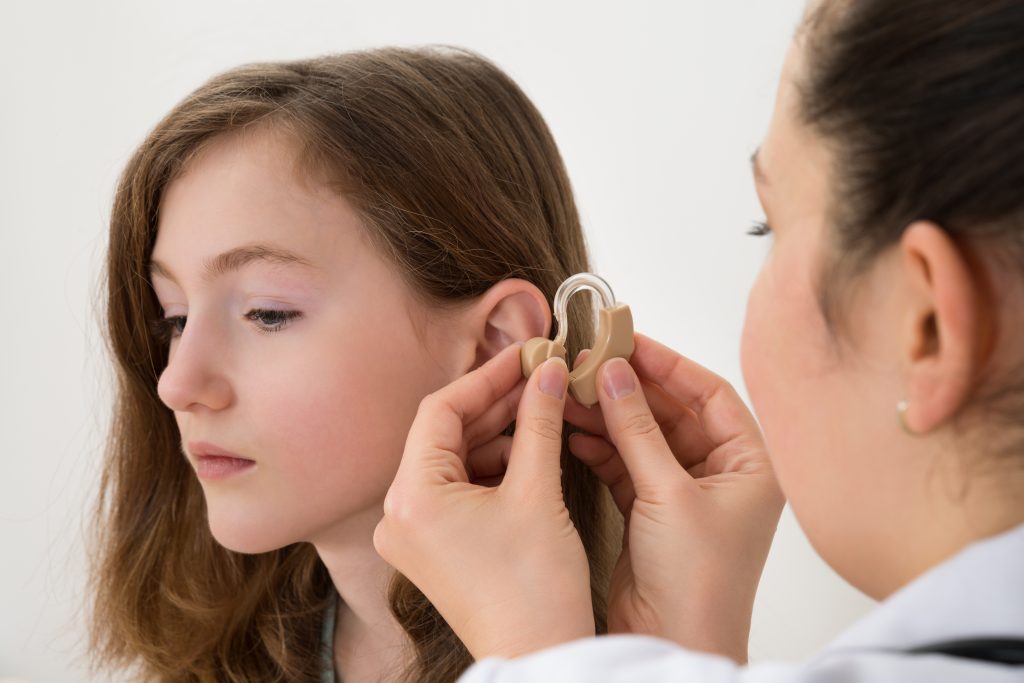
Hearing loss at any age is an emotional issue, and robs you of a sense that adds so much to the richness of life. Hearing loss is especially heartbreaking in children, as well as to the parents whose child have been diagnosed with pediatric hearing loss. Not only does hearing loss impact the sound experience of a life yet to be lived to the fullest, but it also creates a barrier to a child’s number one job: learning.
Fortunately, many causes of hearing loss are treatable, and it is often possible to return the sounds of childhood to a young life.
Categories of Pediatric Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can range from mild (one that causes difficulty hearing hushed tones such as a whisper) to moderate (where the child can still hear loud speech, to a complete loss of hearing).
Hearing loss in children typically falls into two main categories. The most common, a conductive hearing loss, is associated with conditions in the external or middle ear that block the transmission of sound. These conditions can include otitis media, impacted cerumen, a perforated eardrum, or birth defects that alter the structure of the external auditory canal and/or middle ear system. Most conductive hearing losses are medically treatable through either antibiotics and/or surgery.
Sensorineural loss is the second most common type of hearing loss which occurs due to damage to the cochlea (inner ear) and auditory nerve. Sensorineural hearing loss in children is often congenital. Other causes of sensorineural hearing loss include ototoxic medications, premature birth, and illnesses. Sensorineural hearing loss is not medically treatable; however, in most cases, children can be helped with hearing aids or cochlear implant.
A central hearing loss involves the hearing areas of the brain, which have difficulty processing speech and other auditory information. This is often referred to as an auditory processing disorder (APD) or central auditory processing disorder (CAPD).
Symptoms
Signs of possible hearing loss in children range from not startling to loud sounds, to speech delay, to academic difficulties (depending on the age of the child).
Newborn / infant:
- Not startling at loud noises
- Unable to localize sound
- Not showing normal speech development
Toddler and older:
- Speech and language delays
- Academic difficulties/delays
- Needing louder than “normal” volume to hear television
- Needing multiple verbal repetitions
- Stating that he/she is having difficulty hearing
If you believe your child has a hearing loss, please contact our offices in Kennewick, Richland or Walla Walla, Washington to schedule a comprehensive hearing evaluation with one of our Audiologists. Timely hearing testing, diagnosis, and treatment will provide the best course of action ensuring the highest quality life experiences for your child.